“What is a support structure? When do we need one? Which material is it made of?” To answer these questions let us start looking at these one by one, and in the process learn few concepts associated with the idea of support structure.
- What is a support structure?
Imagine printing a model of a person standing upright, printing this layer by layer is possible. But when the person’s arms are spread out, the ink being printed to form the parts of the arm is not going to stay intact against gravity. This is where the support structure plays the role of acting as a platform for the required object to be printed. In additive manufacturing process like ‘Vat photo polymerization’ and ‘Binder jetting’ support structure is automatically created layer by layer irrespective of the requirement.
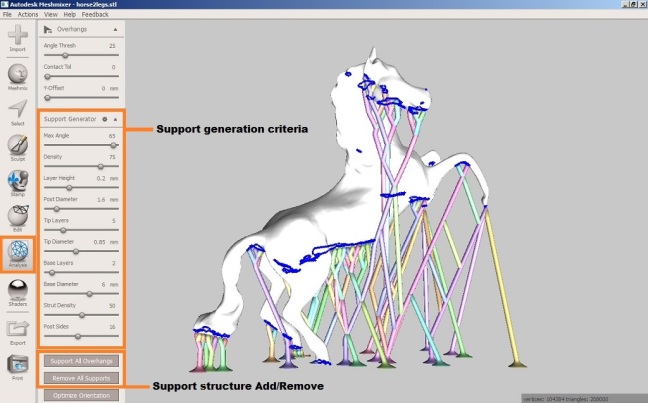
- When do we need support structure?
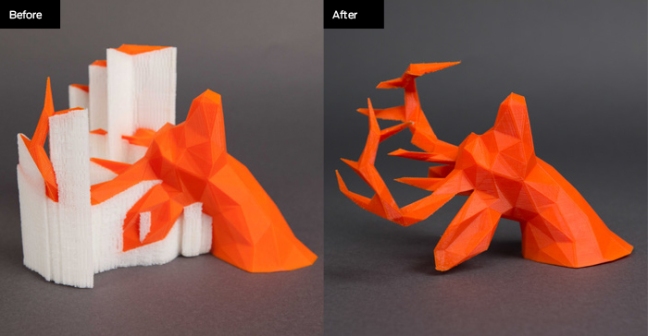
Support structure is very much needed in the ‘Material extrusion’ additive process where the support structures are printed whenever required according to the object being printed. The FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) comes under this category of additive manufacturing. In FDM there is again a single extruder and double extruder which come into picture. A single extruder has provision to print with a single material whereas double has a provision for two.
The single extruder prints the support structure with the same material but with weaker bonds with the main object to make the post processing easy. The double extruder on the other hand prints the object with one material and the support structure with another material which is then separated in post processing.
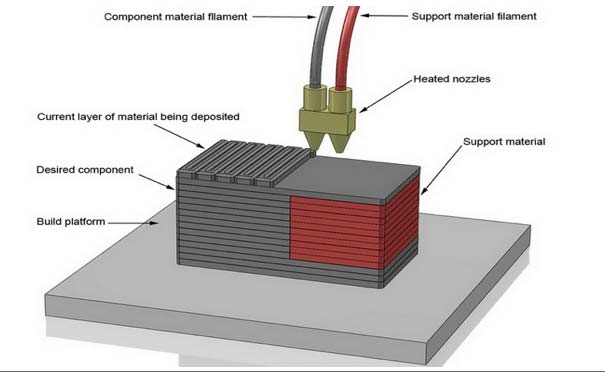
- Which material is used to print the structure?
As far as FDM technology is considered two thermoplastic materials, ABS and PLA are the most used materials in the market. The material of support structure in a single extruder is the same as that of the material. But in double extruder the support structure material is solely decided by the material chosen to print the object. The properties of the object material and the support structure material must complement each other, so as to make separation between them possible during the post process. For ABS, the support structure material normally used is HIPS and for PLA it is PVA. Let us look into few characteristics of these materials.
3.1 ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene):
ABS is stronger and harder than PLA. It requires higher temperature and consistent temperature along the geometry being printed; because of this a heated bed is required to prevent uneven shrinkage, layer distortion and wrapping. ABS is a highly durable and sturdy material.
ABS Features
- Hot plastic fumes when printed.
- Print temperature range: 210 to 250 degree Celsius
- High tensile strength and rigidity.
- Good performance in range of temperature.
- High durability.
- Soluble in acetone.
- Longer shelf life.
- Non-biodegradable but recyclable.
3.2 HIPS (High impact poly styrene):
HIPS is one of the widely used support material used generally in conjugation with ABS, it can be easily removed during post process to arrive at the required object. The support structure is removed by dissolving in limonene or by snapping the support material by hand.
3.3 PLA (Poly lactic acid):
PLA is derived from corn starch, sugarcane, tapioca root making it a bio degradable plastic. It prints at lower temperatures than ABS and also does not require a heat plate. PLA offers minimum flexibility with being little more brittle than ABS.
PLA Features
- Sweet smelling when printed.
- Print temperature range: 180 to 230 degree Celsius.
- Slightly brittle.
- Deforms at high temperature.
- Insoluble.
- Tends to degrade in harsh conditions.
- Biodegradable.
3.4 PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol):
PVA is an odourless, synthetic polymer which is used as support material generally in conjugation with PLA. Even though PVA is slightly more expensive than PLA, its ability to dissolve in water makes removing the support material much easier.
The 3d printing technology and the materials described here are apt examples to describe the concept of support structure printing. There are many other materials which can be used to print the object as well as the support structure. Using support structure while printing with either a single or dual extruder is an important task to get the final 3d printed product right.